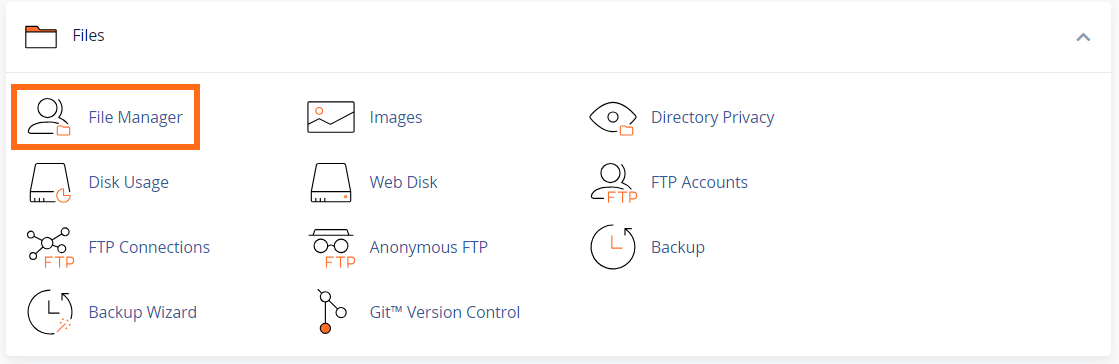
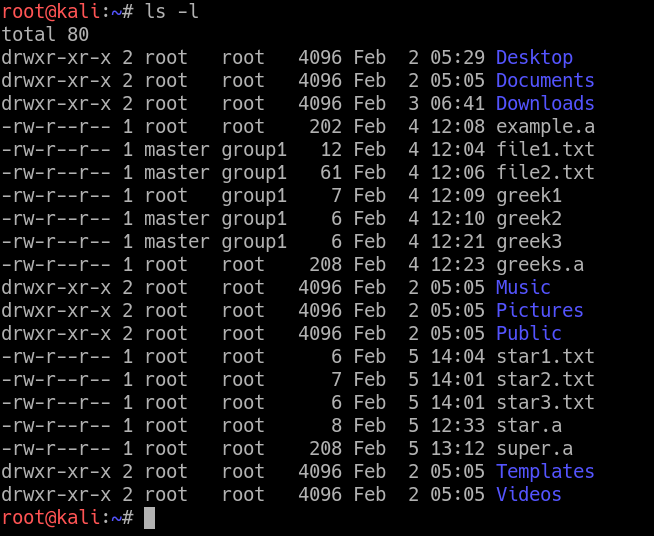
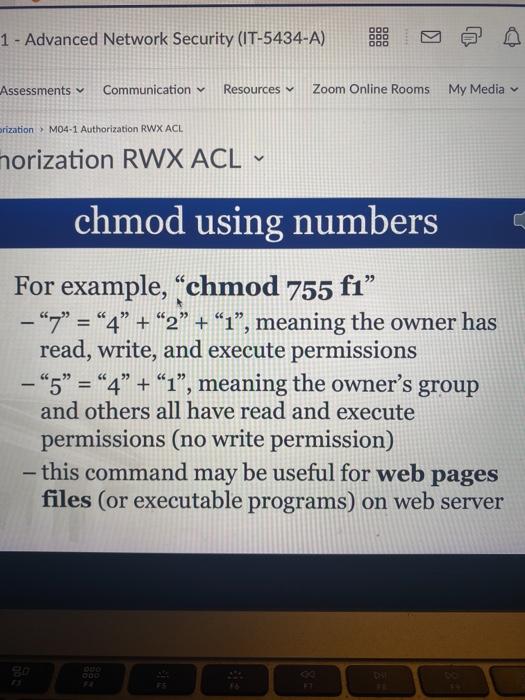
W (write) = 2The command chmod changes the file mode bits of each given file according to mode, which can be either a symbolic representation of changes to make, or an octal number representing the bit pattern for the new mode bits chmod never changes the permissions ofIn Linux, chmod is a builtin command that manages the access permission of file objects The number defined after chmod represents the permissions The chmod 775 is an essential command that assigns read, write, and execute permission to a specific user, group, or others What is the Meaning of chmod 755, and how to execute and verify it is explained in this article

Chmod Command In Linux With Examples Geeksforgeeks
Chmod number meaning
Chmod number meaning-The standard UNIX way to show that a number is octal is to start it with a zero GNU chmod will assume the mode you're giving it is octal anyway, but it's safest to prepend the zero Finally, if you see a at the end of the modestringrwxrxrx then that means the file has extended permissions, and you'll need more than chmod Chmod numbers meaning Basically, an user group can hold three kind of permissions on a file or directory One can either read (r), write (w) or execute (x) the file But these permissions has to be set for each groups of users Owner, Group, Other Every time you need to chmod a file or directory, you need to specify permissions for each groups




Linux Commands Chmod Cloudaffaire
Answer (1 of 6) WELL this is a command to change the permission of a file chmod stand for the change mode and 775 means you are giving the permission to the file r stand for read its value is 4 w stand for the writeits value is 2 x stand for the executeits value is 1 it u give 7This person cannot read, write, or execute the file 1 = execute onlyThe chmod command uses a threedigit code as an argument The three digits of the chmod code set permissions for these groups in this order Owner (you) The sums of these numbers give combinations of these permissions 0 = no permissions whatsoever;
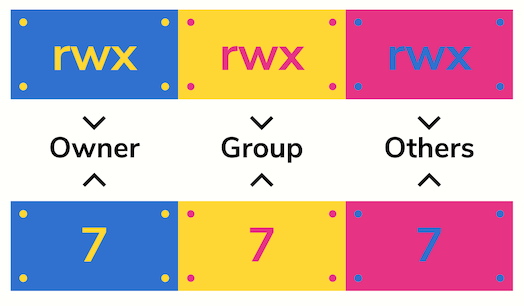
Chmod calculator generates command in number format for file and directory permissions in Unix and Linux If you are working on Unix, Linux server then permissions are a very important and difficult task Our chmod calculator generates file permissions for owner, group, and the public in number (744) and symbolic (rwxrr) notation formats7 read, write and execute rwx 111 6 read and write rw 110 5 read and execute rx 101 4 read only r 100 3 write and execute wx 011 2 write only w 010 1 execute only x 001 0 none 000 Want to know what the numbers in chmod mean?
What each chmod number means * 4 = Read * 2 = Write * 1 = Execute There mat be a fourth number on the end this has the following meaning 4 = Set user ID on execution to grant permissions based on the files owner, not the user who created the processView (u)ser, (g)roup and (o)thers permissions for chmod 700 (chmod arwx,grwx,orwx) or use free online chmod calculator to modify permissions easily chmod 775 /path/to/file chmod command uses & Explanation chmod is a command to change permission of a file It stands for change mode The number "775" is to provide permission to the file There are three type of permissions r stand for read its value is 4 w stand for the writeits value is 2 x stand for the executeits value is 1




Learning The Shell Lesson 9 Permissions



How To Change Permissions Chmod Of A File Hostgator Support
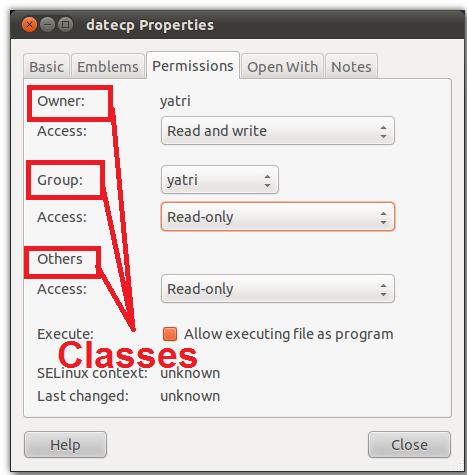
Please note that chmod 777 filename is the equivalent of chmod 0777 filename in this example The first octal digit sets the setuid, setgid and sticky bits (see this article for more details on setuid/setgid) octal 2 means to set group ID on the file So, the equivalent would be to do a chmod arwx filename, then chmod gs filenameThe chmod info page does explain this in more detail The permission number can consist of three or four digits, ranging from 0 to 7 When 3 digits number is used, the first digit represents the permissions of the file's owner, the second one the file's group and the last one all other users The write, read, and execute permissions have the following number value r (read) = 4;The command to use when modifying permissions is chmod There are two ways to modify permissions, with numbers or with letters Using letters is easier to understand for most people When modifying permissions be careful not to create security problems Some files are configured to have very restrictive permissions to prevent unauthorized access



1




Understanding Unix Permissions And File Types Unix Linux Stack Exchange
Using flags is an easy and short form to set user permissions This article(I hope) puts it SIMPLE, if you want to learn the theory, also visit the links in the end There are four OCTAL (07) digits, which control the file permissions But often, only three are used If you use 600 it equals 0600 600 permissions means that only the owner of the file has full read and write access to it Once a file permission is set to 600, no one else can access the file Example chmod commands (in octal and symbolic notions) setting permissions to 600 chmod 600 exampletxt chmod u=rw,g=,o= exampletxt chmod arwx,ux,grwx,orwx exampletxt Copy The chmod command allows you to change the permissions on a file using either a symbolic or numeric mode or a reference file We will explain the modes in more detail later in this article The command can accept one or more files



Understanding Linux Permissions And Chmod Usage




A Unix And Linux Permissions Primer Daniel Miessler
Instead of using ugoa shorthand for permissions, chmod allows you to use numbers, which is called octal mode number notation File permissions in Linux are stored in file mode bits , and those bits varies between user groups In Unixlike operating systems, the chmod command is used to change the access mode of a file The name is an abbreviation of change mode Syntax chmod referenceoperatormode file The references are used to distinguish the users to whom the permissions apply ie they are list of letters that specifies whom to give permissions C an you provide more information about chmod command octal mode number notation?




Permissions In Linux Geeksforgeeks




Unix File Permissions Computer Science
"chmod hexadecimal" Code Answer's ubuntu chmod codes shell by Outrageous Opossum on Donate 1 Source enwikipediaorg chmod values whatever by slgotting on Donate 1 Whatever queries related to "chmod hexadecimal" chmod linux examplerwrwSr chmodChmod numbers meaning Basically, an user group can hold three kind of permissions on a file or directory One can either read (r), write (w) or execute (x) the file But these permissions has to be set for each groups of users Owner, Group, Other Every time you need to chmod a file or directory, you need to specify permissions for each groups This article explores chmod 777, a Linux command used to give ALL RIGHTS to the user, group, and others As a new Linux user, web developer, or system administrator, you have probably been instructed to type chmod 777 /path/to/file/or/folder into your Linux shell at some point Whenever you're running commands on your systems (especially as root!), you should




An Introduction To Linux File Permissions Boolean World




Definition Of Chmod Pcmag
View (u)ser, (g)roup and (o)thers permissions for chmod 644 (chmod arwx,ux,gwx,owx) or use free online chmod calculator to modify permissions easilyThe numbers in chmod tell the computer which ones to check off Let's say these are your empty check boxes the number 5 is represented in binary as '0101' in four bits, so you can use them to fill in certain boxes without a complicated process This command will return all files/directories in with sticky bit set linuxhandbook~$ find perm /1000 If the directory doesn't have the execute permission set for all, setting a sticky bit will result in showing T instead of t An indication that things are not entirely correct with the sticky bit Conclusion




Linux Commands Chmod




What Is Chmod 777 How To Change File Permissions For Linux
chmod R or *page Numerical Shorthand Another way to use chmod is to provide the permissions you wish to give to the owner, group, and others as a threedigit number The leftmost digit represents the permissions for the owner With chmod 755 you're using octal numbers, the binary representation of which is used to set specific bits of permissions First (left) 3 bits correspond to owner permissions, middle 3 to the group permissions, and last (rightmost) correspond to permissions of all other usersWhat is CHMOD and what do the numbers mean?



What Is Chmod 777



Chown Wikipedia
There's actually 4 attribute sets you can work with via chmod Special, User/Owner, Group, and Others in that order, when working with the fournumber chmods, with that first number being special bits that can be set chmod 4555 equates to the following Set UID bit Run the file as the owner regardless of which user is running it In short, "chmod 777" means making the file readable, writable and executable by everyone chmod 775 /path/to/file Hopefully, this article can help you understand better about the file permissions in Unix system and the origin of the magical number "777"Chmod Calculator Chmod Calculator is a free utility to calculate the numeric (octal) or symbolic value for a set of file or folder permissions in Linux servers How to use Check the desired boxes or directly enter a valid numeric value (eg 777) or symbolic notation (eg rwxrwxrwx) to see its value in other formats File Permissions




Why Not To Use Chmod 777 Pi My Life Up



What Does Chmod 755 Do Quora
Chmod by the Numbers chmodby the Numbers Up to this point, we've been setting the mode with letters It turns out that you can also set the mode numerically Here'show it works Write the permissions you want the file to have To make yourlife easier, write the permissions grouped into sets of three letters* This article focuses on chmod using 3 numbers If you're looking to have to use 4 numbers, to set a sticky bit, SUID or SGID, you will need to see the third article in this series link here When made up of 3 numbers, each of on the "octals" represents each of the groups that have access to a file For example the octal 724 presents a situation where 7 is the octal for setting Owner The chmod command lets you "change the mode" – another way to describe access permissions To do this, open the Terminal and type the following chmod 777 / path / to / file




16 04 How Do I Use Chmod To Make Sh Files Executable Ask Ubuntu




Chmod 644 755 777 What S The Difference Linuxpip
Yes different chmod ax will add the exec bits to the file but will not touch other bits For example file might be still unreadable to others and group chmod 755 will always make the file with perms 755 no matter what initial permissions were ThisChmod number meaning Want to know what the numbers in chmod mean?Zen Cart Support What is CHMOD and what do the numbers mean?



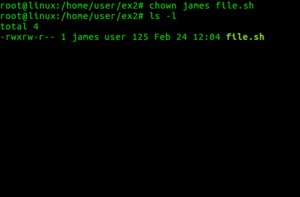
Chown Command In Linux With Examples Geeksforgeeks




Learn Why You Shouldn T Use Chmod 777 How To Find Out Learning Reading Writing
This video attempts to explain what the "chmod" numbers mean that are often used but never explained in guides and installation instructionsNote Yes, I did



1




What Does Chmod 755 Do Quora




Understanding File Permissions What Does Chmod 777 Mean Make Tech Easier




Chmod Umask Stat Fileperms And File Permissions




How Did The Number 777 In Chmod 777 Come Out Under Linux Develop Paper




Linux Permissions Making Sense Of 755 And Rwxr Xr X Serverwise




Linux File Permissions Complete Guide Devconnected




Chmod X Explained Everything You Need To Know




Chmod Command In Linux File Permissions Linuxize




Chmod Options Permissions Files Linux Pocket Guide Book




Command Line Understanding Chmod Symbolic Notation And Use Of Octal Ask Ubuntu




Modify File Permissions With Chmod Linode




File Permission Meanings Stack Overflow




How To Set Chmod 777 To A Folder And All Its Contents Dev Community




Chmod 755 Command What Does It Do Codefather



Unix Permissions The Easy Way Index Of All Chmod Permutations By Semi Koen Towards Data Science



What Does Chmod 400 Mean Quora



Linux File Permissions And Chmod Doug Vitale Tech Blog




Understanding File Permissions What Does Chmod 777 Mean Make Tech Easier




Ownership And Permissions




What Is Chmod 777 How To Change File Permissions For Linux




Understanding File Permissions What Does Chmod 777 Mean Make Tech Easier




Changing File Permissions Wordpress Org




When To Use Chmod Vs Chown Cbt Nuggets




The Basics Of The Chmod Command Pi My Life Up




How To Use The Chmod Command On Linux




What Is Umask And How To Use It Effectively Liquid Web
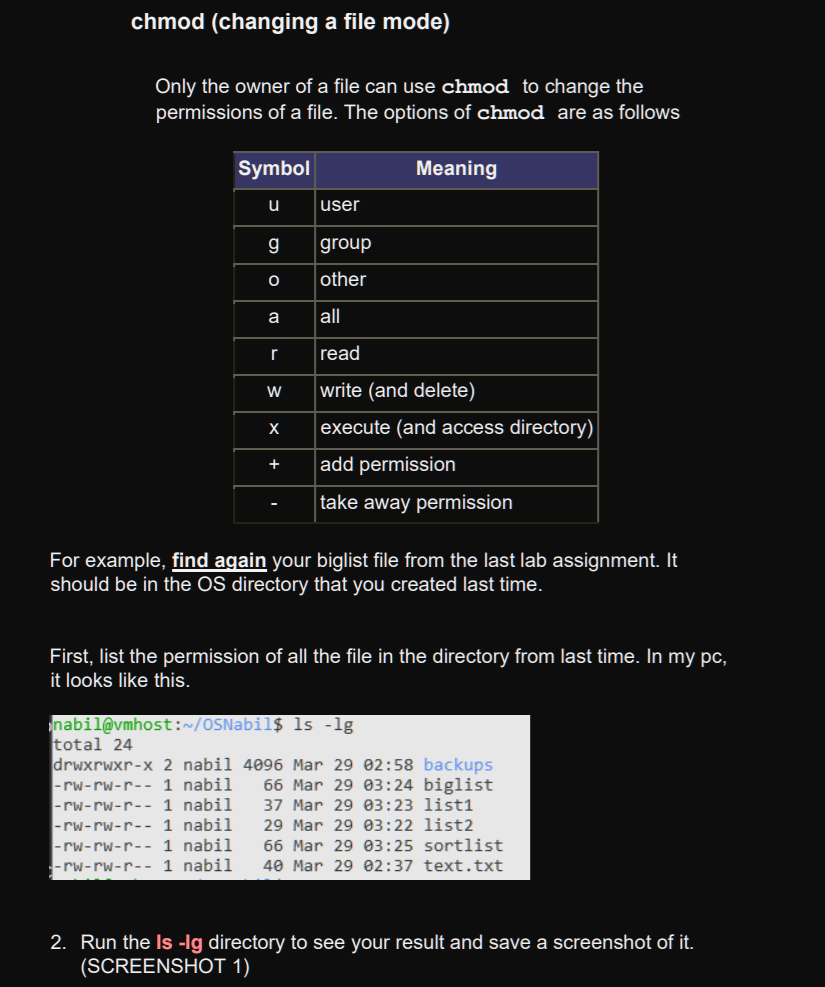



Chmod Changing A File Mode Only The Owner Of A File Chegg Com




Chmod 755 775 Recursive Ssh Permissions Chmod 775 Vs 777




What Does Chmod 777 Mean Linuxize



1 Advanced Network Security It 5434 A Assessments Chegg Com




Your Own Linux Chmod Basics Of Files Directories Permissions And Use Of Chmod



Everything About Chmod Command In Linux Hackerearth




Linux Chmod Command Linux Permissions




Chmod 644 755 777 What S The Difference Linuxpip




Linux Commands Chmod Cloudaffaire




Unix Permissions The Easy Way Index Of All Chmod Permutations By Semi Koen Towards Data Science




Linux Chmod Command Help And Examples



14 Permission And Modification Times




Understanding Basic File Permissions And Ownership In Linux The Geek Diary




Basics Of Linux File Permission Linux Is A Multi User Operating System By Madeesha S Tech Space Medium




How To Use The Chmod Command On Linux




08 What The Chmod Numbers Mean Youtube




How To Use Chmod Command In Linux Explained With Examples




Linux File Permissions Complete Guide Devconnected




Command Line Understanding Chmod Symbolic Notation And Use Of Octal Ask Ubuntu



Chmod 777 What Does This Mean Learn Linux Permissions Easy Way




Understanding File Permissions



What Is The Chmod 777 Filename Sh Used For Quora




Understanding Linux Permissions And Chmod Usage




File Permissions In Linux Unix How To Read Write Change



Linux File Folder Permissions




How To Use Chmod And Chown Command In Linux Nixcraft




Understanding Linux Permissions And Chmod Usage



How To Change Permissions Chmod Of A File Hostgator Support




Permissions In Linux Geeksforgeeks




Quick Answer How To Use Chmod In Linux Os Today



Fun With Numbers In Chmod




Solved Part 3 Permissions For Files Follow The Instructions Chegg Com




Chmod Command In Linux With Examples Geeksforgeeks




What Is Chmod 777 How To Change File Permissions For Linux




Linux Permissions An Introduction To Chmod Enable Sysadmin



Symbolic Notation Geometry




Chmod Cheatsheet Linux



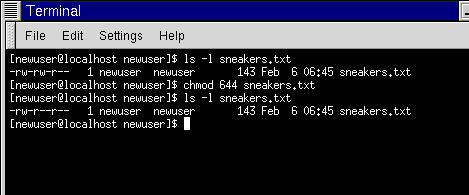
What Is The Meaning Of Chmod 755 And How To Execute And Verify It




9 Quick Chmod Command Examples In Linux




Chmod X Explained Everything You Need To Know



What Does Chmod 775 Mean Quora




How To Use Chmod Command In Linux Explained With Examples




Chmod Calculator Chmod Generator Chmod Command




Chmod 777 A Definitive Guide To File Permissions




Unix Linux Os X File Permissions




File Permissions Mode 0777 Vs 777 Digital Fortress




Understanding Linux Permissions And Chmod Usage




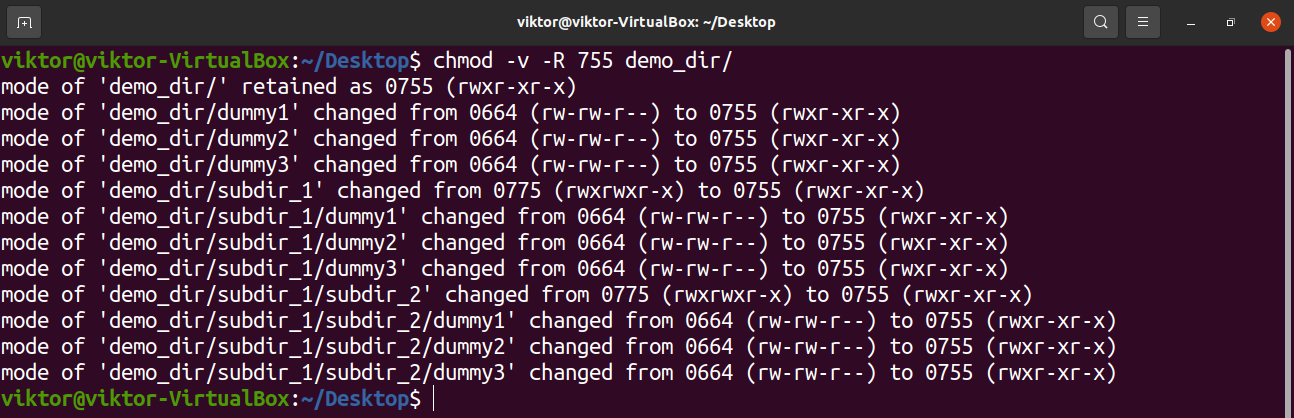
How To Recursively Change The File S Permissions In Linux Linuxize



Unix Tutorial Five




Unix Permissions




Linux Chmod File Permissions Decoded From The 1980s Rickyadams Com




How To Use Chmod Command In Linux Explained With Examples




Command Line Understanding Chmod Symbolic Notation And Use Of Octal Ask Ubuntu



Chmod
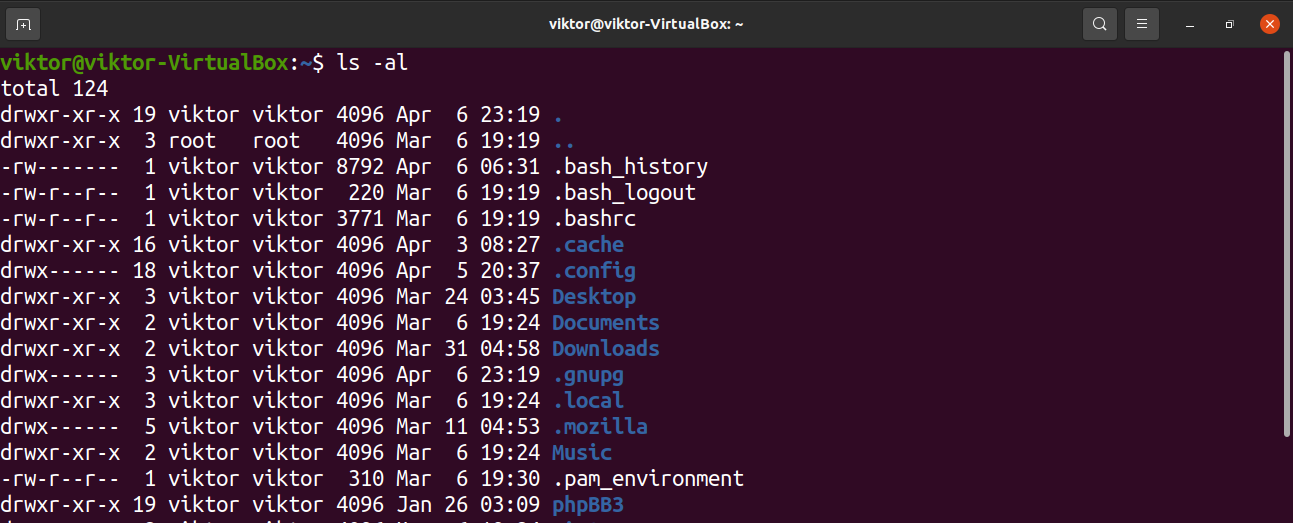



What Is The Meaning Of Chmod 755 And How To Execute And Verify It




Understanding Linux Permissions And Chmod Usage




Chmod 755 Command What Does It Do By Claudio Sabato Medium



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿